6 4: Issuing Stock for Non-Cash Assets Business LibreTexts
During negotiations, officials for Maine offer to issue ten thousand shares of $1 par value common stock for this property. The shares are currently selling on a stock exchange for $12 each. The investor decides to accept this proposal rather than go to the trouble of trying to sell the land. The most common example of common stock being sold by a company is for the exchange of cash. A company will take those funds and invest them into the business by applying the cash to new investments. In the most simple form, you will see a deposit into the firm’s bank account and then issuance of common stock, i.e. an increase in the company’s capital.
4: Issuing Stock for Non-Cash Assets
Each share of the company’s common stock is sellingfor $25 on the open market on May 1, the date that Duratechpurchases the stock. Duratech will pay the market price of thestock at $25 per share times the 800 shares it purchased, for atotal cost of $20,000. The following journal entry is recorded forthe purchase of the treasury stock under the cost method.
What is the Accounting for Issuance of Common Stock?
- To offset this addition to assets, you’ll then increase shareholders’ equity by the same amount.
- The deficit of $2 per share ($8 minus $10) is called a discount on common stock.
- The company may want to increase the share price by increase the demand by buying them back.
- This accounting treatment also differentiates this finance source on the balance sheet.
- The Walt Disney Company hasconsistently spent a large portion of its cash flows in buying backits own stock.
- The company spends $ 5.5 million to purchase the shares and keep them on the balance sheet.
Any finance received in excess of the share’s par value ends up on the share premium account. This account includes any compensation received over that value. If companies issue shares at below the par value, this account will also get impacted. In most cases, the share premium account involves recording excess funds received from new share issues. Overall, common stock is a security that represents a company’s ownership.
Issuing no-par common stock
When the share has no par value, all the issuance prices will be recorded into the common stock. Par Value or Face Value or nominal value is the value state on the share or bond. Common Share par value is the legal value state in the company article of memorandum. Total stock par value is the amount that protects the corporate creditor in the case of liquidation. The shareholders are not allowed to withdraw the total capital from the company.

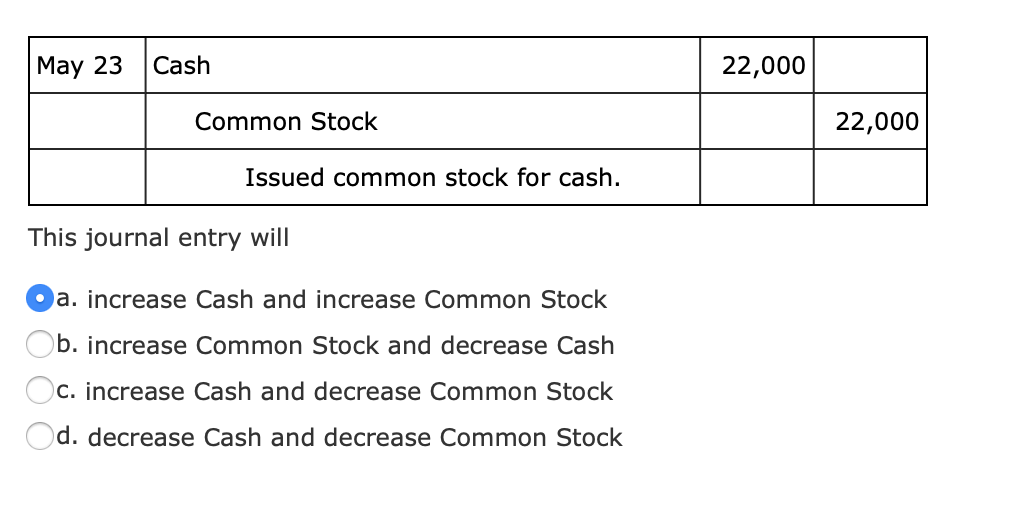
Journal entry for issuing common stock
However, it does not mean that company needs to issue all the authorized shares. 1Although the Kellogg Company has its headquarters in Battle Creek, Michigan, the company is incorporated in the state of Delaware. Thus, the laws of Delaware set the rights of the common stock shares for this company. After buying back Kevin’s shares, ABC decides to retire the shares on July 31. After Board approval, ABC’s accounts team would prepare the following journal entry. The first example we will go through is the sale of common stock by ABC Ltd for cash.
The first will be using the cost method where a company is buying some of their own shares and later reissues them. In this case, we need to consider any gains or losses the company experienced in the transaction. In the second example, we’ll assume the company will retire the shares it buys back, so we’ll be using the constructive retirement method.
In an acquisition situation, we will often see the exchange of shares for shares. For example, company A will acquire company B, giving company B shareholders a mix of company A shares and cash. For example, the company ABC issues the above shares of common stock for $100,000 which is at the price of $5 per share instead of $1 per share. Occasionally, a corporation will buy back its own shares on the open market.
For example, Kellogg discloses a par value of $0.25 for its common stock, which is actually quite high. Many companies report par values that fall between a penny and a nickel. The balance sheet for Barnes & Noble shows a par value for its common stock of one-tenth of a penny. There are no application or allotment accounts we have to deal with. You certainly could, but when only dealing with one new shareholder and the balance is paid in full at the exchange, these additional accounts would only add complication.
The most mysterious term on a set of financial statements might well be “par value.” The requirement for a par value to be set was created decades ago in connection with the issuance of stock. It is printed on the face of a stock certificate and indicates (again depending how to determine the cost per unit chron com on state law) the minimum amount of money that owners must legally leave in the business. The debit to the Treasure Stock account reflects the new asset ABC Ltd holds in its own stock. And the credit reflects the company pays Kevin to buy his position out.
When the company performs well, it will be able to raise more funds by issuing more stock. Company can raise money to expand the business and continue operation by issuing common stock to the investors. A group of investors is not able to raise enough money to operate business in a big scale, so they need to raise more capital from the market with thousands of investors. The company can retire stock by buyback the outstanding stock from the market.

Leaver a comment